PCI supports three types of address spaces:
-
Memory Address Space
- PCI devices map into the CPU’s memory address space.
- Can support 32-bit or 64-bit addresses.
- x86 CPUs can access this directly.
-
I/O Address Space
- PCI supports 32-bit I/O addresses, but x86 CPUs traditionally use 16-bit I/O.
- Many platforms limit I/O space to 64 KB (16-bit to match CPU).
- Allows devices to perform simple I/O operations using CPU instructions.
-
Configuration Address Space
- Special address space for device configuration and control.
- Each PCI function has internal registers visible to software.
- Provides a standardized, plug-and-play mechanism.
- Size: 256 Bytes per function.
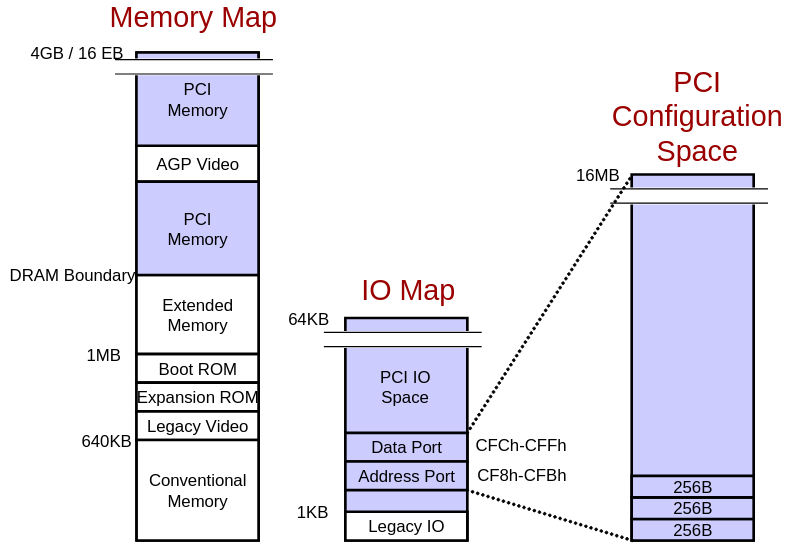
PCI System Limits
- Functions per device: 8
- Devices per bus: 32
- Buses per system: 256
- Total configuration space: 16MB
How CPUs Access Configuration Space
-
Legacy PCI (x86 CPUs)
- Cannot access configuration space directly.
- Uses indirect I/O access:
- Configuration Address Port: CF8h–CFBh
- Configuration Data Port: CFCh–CFFh
-
PCI Express (PCIe)
- Configuration space can be memory-mapped, allowing direct CPU access.